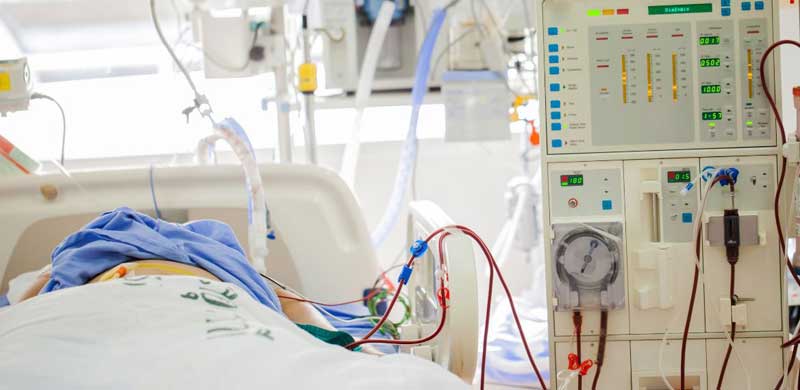
Dialysis (Hemodialysis & Peritoneal Dialysis) & advances
Dialysis is a medical treatment used to replace the function of the kidneys when they are no longer able to filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood. There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Hemodialysis involves circulating the patient’s blood through an external machine equipped with a filter, called a dialyzer, to remove waste products and excess fluid. This procedure is typically performed at a dialysis center several times a week.
Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of the abdominal cavity (the peritoneum) as a natural filter. A special fluid is introduced into the abdomen, which absorbs waste and excess fluid, and is then drained out. This type of dialysis can be done at home, often overnight, offering greater flexibility for patients.
Recent advances in dialysis technology have led to improvements in the efficiency and comfort of both treatments. Innovations include more portable dialysis machines, more effective dialyzers, and better biocompatible dialysis fluids. Furthermore, wearable artificial kidneys and advancements in home-based peritoneal dialysis are paving the way for more convenient and personalized dialysis options, improving the quality of life for patients with kidney failure.